Typical structural systems
Wood products are suited to almost all new-build and renovation construction. Wood structures can be used in different applications in buildings, be they tall tower blocks, large halls or bridges. In addition to structures, common uses for wood products are windows and doors, interior decoration and furniture. Building standards regulating the use of wood vary from country to country.
There are many industrial alternatives for the construction of wooden buildings, from which the optimal solution for a specific case can be chosen. Common to them are highly developed industrial prefabrication and fast construction. A wooden building can be built in half the time required for traditional construction.
Load-bearing walls
In wooden buildings, the most commonly used frame system is a storey-based system based on load-bearing walls. The load-bearing walls can be built with large pole-structured elements or elements made of solid wood. With wooden intermediate floor structures, spans of up to seven metres can be achieved. Load-bearing lines are usually the external walls of the building and some of its partition walls, normally the walls between apartments. The floors and some of the walls serve as structures boosting the house’s rigidity.
A Pole-framed element house

A pole-frame element is the most common way to make a wood-framed building. In tall buildings, the wall frame is made of standard-dimensioned glued laminated timber. This can be used to construct buildings of more than four storeys. The load-bearing and non-load-bearing walls are structurally identical. The intermediate floor structures can be freely selected. It may be, for example, a beam floor, box slab or ribbed slab. Long spans are possible by increasing the height of the load-bearing structure. Spans can also be increased with a composite concrete and wood structure or so-called hybrid structure. Experience of pole-framed structures is very long. With a pole structure, excellent energy efficiency and air-tightness can be achieved, right up to the level of a passive house. The technology is flexible for different needs. Structural solutions and types can be optimised according to the application. Wood structures also work together with concrete structures. Together with other materials, hybrid structures are further diversifying the possibilities for the use of the structure. With engineering wood products, the sagging of structures is slight. The high degree of prefabrication of the elements guarantees fast erection. A house can be erected at a rate of one storey per week. Installation on the building site can be done protected from the weather.
A Solid wood apartment block using CLT technology
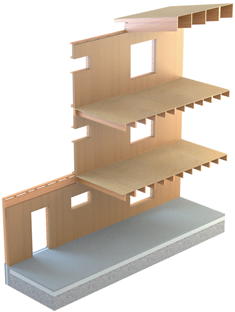
The load-bearing walls can be built with CLT solid wood boards, in which the layers of wood are glued crosswise (CLT: cross laminated timber). The board acts as both a method of building wooden apartment blocks and as a stiffening structure in walls and floors. Openings and joints are made on the boards at the factory using precise computer-controlled milling technology. The maximum size of a CLT board is 3 x 16 metres and it is available in many different strengths. The use of CLT board enables the flexible opening of walls, intermediate floors and cantilevered structures. The capacity of the board is sufficient for buildings of up to 12 storeys. Elements are delivered in the desired degree of readiness, including insulation, surface materials, windows and doors. Delivery may also include installation. CLT is common construction technology in Germany and Austria, for example. In German-speaking countries, the technology goes by the name of KLH (Kross Laminate Holz).
Column-and-beam system

In a column-and-beam system, the building’s frame comprises glued laminated timber columns and beams, on to which the intermediate floor, roof structures and external walls are built. The rigidity of the frame is usually achieved with diagonally installed stiffening joints or mast columns. With a column-and-beam system, it is possible to achieve an open, convertible floor solution and large openings in facades. The system enables free and flexible spatial planning and the opening up of walls. Because there are no load-bearing partition walls, it is easy to change the position of walls between apartments during the life cycle of the building. The structural system offers good flexibility in conversion. Because of the single-dimension vertical structures, the building does not sag anywhere. The construction stage on the building site is very fast. The roof can be installed in just a few days, after which the house has protection from the weather. The external walls are installed as large lightweight elements. The thickness of the insulation and external cladding material can be selected by the customer.
Volumetric elements
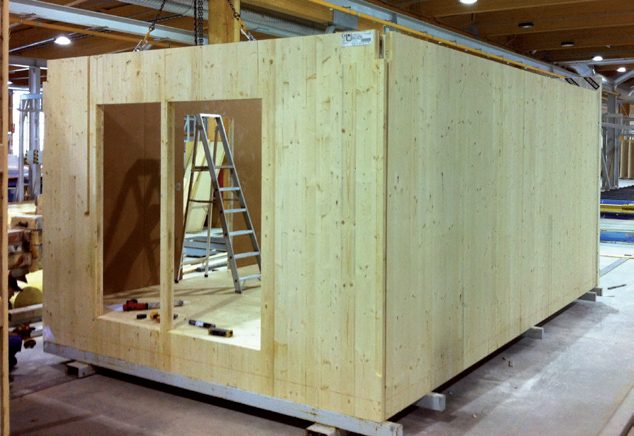

Volumetric element technology is a construction method in which a building is assembled separately in a factory from ready-to-assemble box units. A volumetric element usually consists of a load-bearing frame and limiting surfaces: ready walls, floors and a roof. The elements are completely manufactured in factory conditions, protected from the weather. Windows, HVAC and electrical equipment and fittings are all installed in the element at the factory. The load-bearing structure of a volumetric element can be built in many different ways, for example using column-and-beam technology, a frame structure or large slab-like elements. With volumetric element technology, excellent sound insulation can be achieved because of the double structure. The typical maximum dimensions of volumetric elements are 12 x 4.2 x 3.2 metres. In the planning of the dimensions of elements and modular systems, the restrictions set by the transportation of the elements must be borne in mind. Volumetric element technology is very suitable for residential houses and dwellings. The construction stage on the building site is very fast. Because of its speed, the system is excellent in infill development and, for example, building additional storeys. It is also suited to low-energy construction. Volumetric element technology is, for example, a common method of building wooden apartment blocks in Sweden.
Log structures
Log construction is a traditional method of wood construction, especially in countries where there is a plentiful supply of cross-sectionally suitable and straight wood. In a log house, the building’s load-bearing structures at least are made of log.
The types of log used in log buildings are:
- Round log: a round-sided log formed manually or mechanically. The diameter of an industrial round log is the same from base to tip.
- Squared log: a log formed with flat sides. Can also be cut traditionally by hand using a cant saw.
- Deadwood log: log made of dried-out pine
- Laminated log: a wood product made by gluing together several layers of wood
Round log is mainly used in holiday cottages, storage buildings and barns. Round logs are built into corners using a method by which the log crosses the log on the transecting wall and protrudes out from the corner by some distance.
Laminated logs are made by glueing together several layers of wood and planing the log into the desired profile. Benefits of this structure include homogeneous properties and, in some types of log, also very little sagging or settling.
Squared log represents traditional labour-intensive construction. It is normally used in buildings that need to be tight, such as residential and holiday dwellings, granaries, saunas, etc. A squared-log building is more even along its walls than a round-log one, so it is easier to attach cupboards to the walls, for example. The overlapping corner sections of squared logs are also usually shorter than those for round logs, which saves on timber. Short corner sections are, for example, of the dovetail and locking type.
In Finland, logs are usually made of pine.